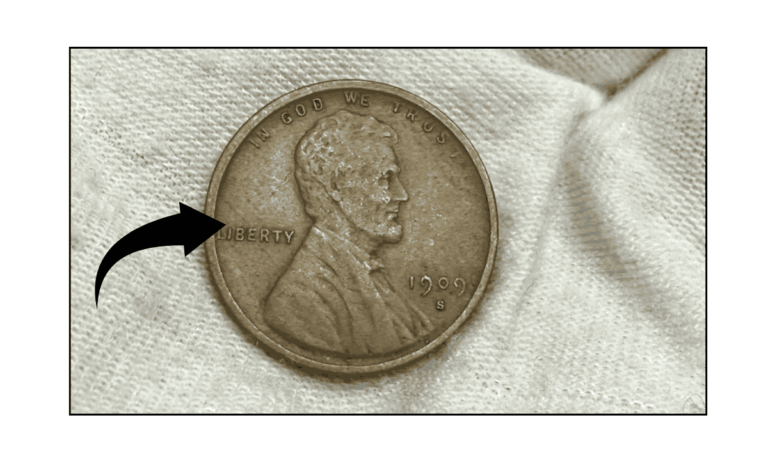
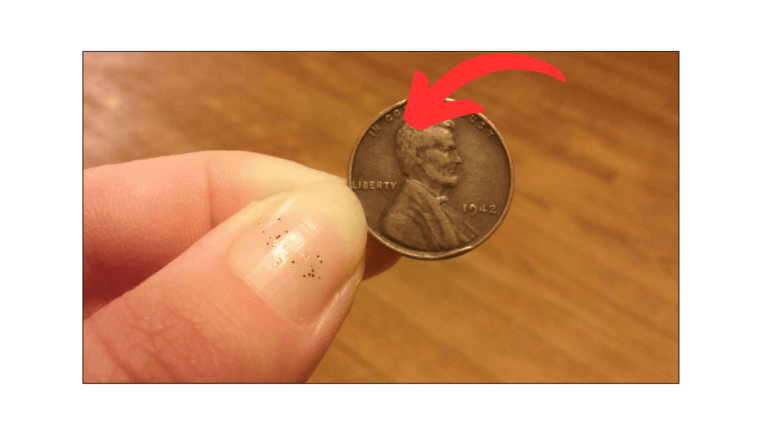
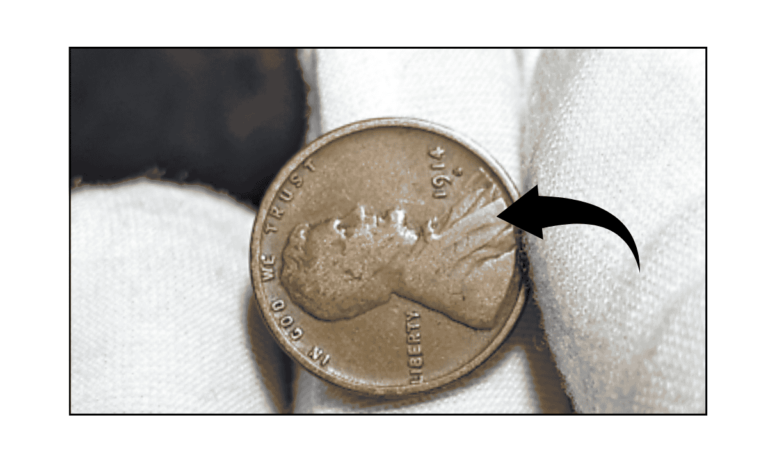
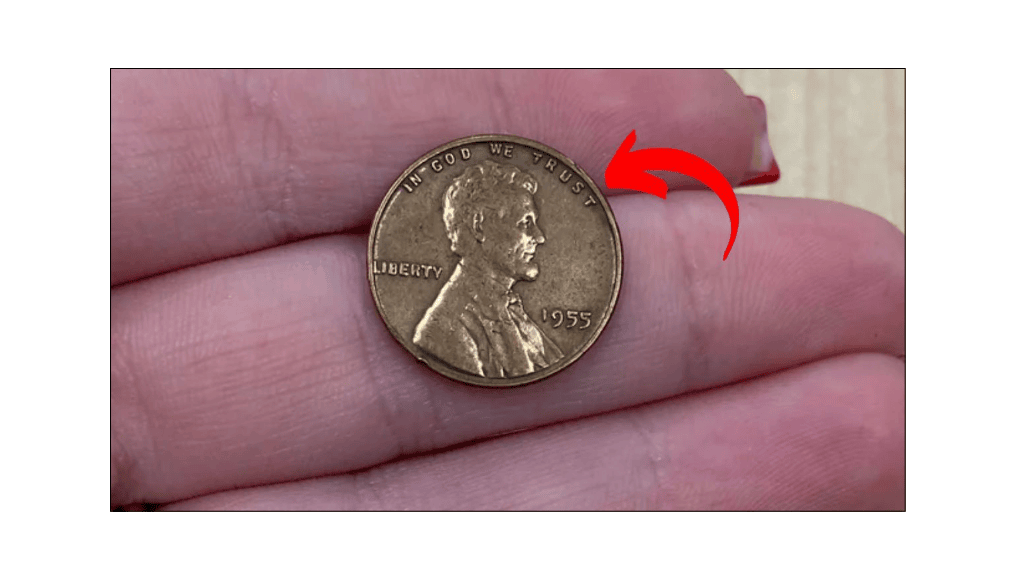
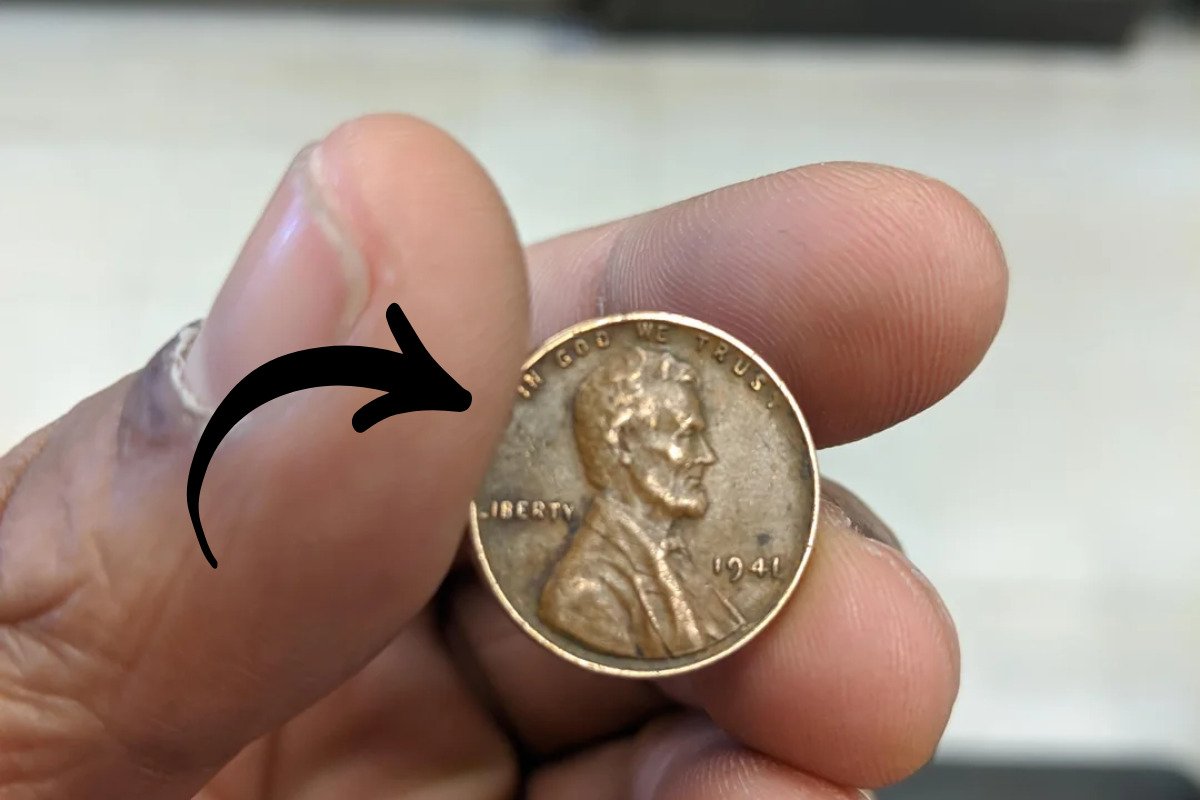
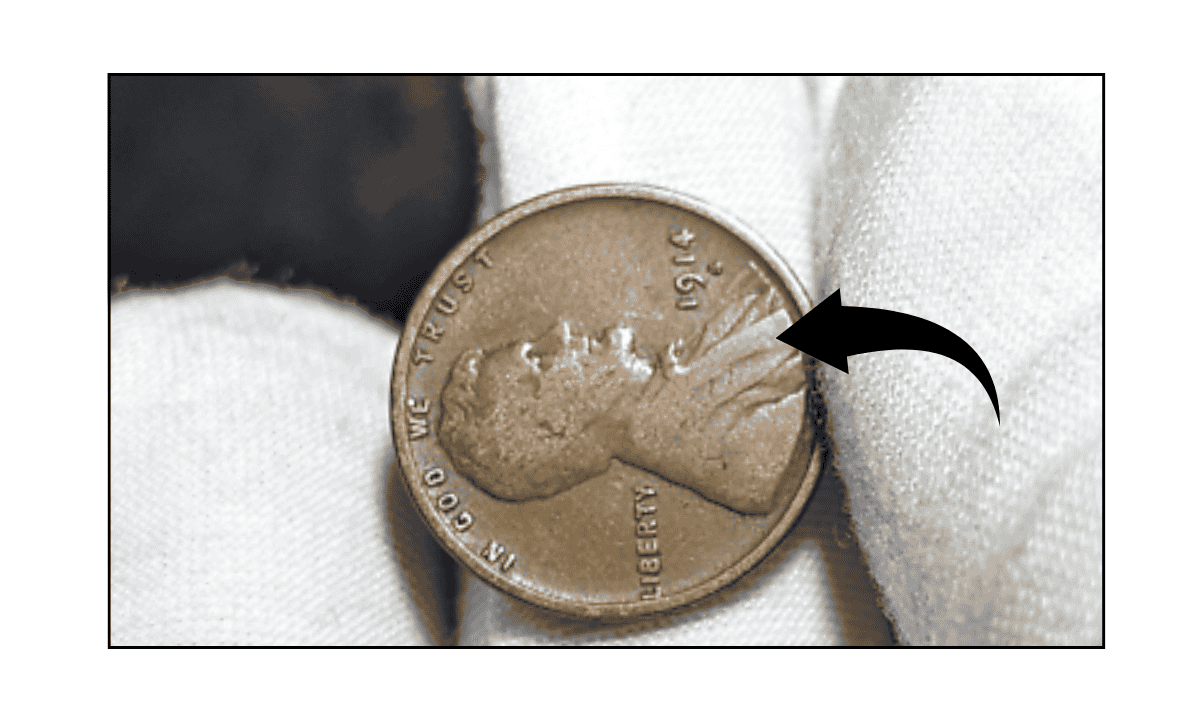
The Lincoln Wheat Penny Valued at $224K, Still in Circulation
If you’re into coin collecting or simply love rare treasures, there’s one coin that stands out for its unique mistake and high value — the 1958 Doubled Die Lincoln cent. This rare penny is not just a collector’s dream but …