Última publicación
Mallorca vs Espanyol: duelo clave en Son Moix por Europa y la permanencia
El RCD Mallorca y el RCD Espanyol se enfrentarán este sábado a las 16:15h en Son Moix, en un partido...
Mallorca y Espanyol se juegan mucho en la jornada 28: previa y detalles
El Espanyol viaja a Palma para enfrentarse al Mallorca en un partido clave de la jornada 28 de LaLiga EA...
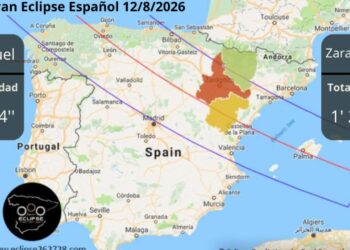
España se prepara para un eclipse solar total en 2026
Desde tiempos ancestrales, los eclipses han sido interpretados como señales de los dioses o presagios de grandes cambios. Hoy en...
Fin de semana clave para el fútbol base del Espanyol
El fin de semana del 15 y 16 de marzo será determinante para los equipos del fútbol base del RCD...